2024年11月,737机队发生1起右主起落架收放作动筒放下液压软管和支架相磨出现漏油,导致A/B系统液压油大量渗漏和前轮转弯无法工作的案例。通过进一步的机队普查,发现多起主起落架收放作动筒液压软管以及起落架上方刹车软管和导向支架相磨的情况。为了避免管路磨损漏油导致的AOG事件,特编写材料做一提示。
概述:飞机落地前实时监控液压A系统液压油量低和A系统EDP低压警告,落地后机组反映前轮转弯无法工作,飞机拖回。地面检查A系统液压油量0,B系统油量16。检查右主起落架收放作动筒放下管路漏油。
分析:结合系统原理图,当起落架放下后,来自起落架选择活门的压力油经过软管供到主起收放作动筒放下端,在3000PSI高压下,A系统油量快速下降。飞机落地后机组参考检查单将备用前轮转弯电门放备用位,转换活门作动导致B系统压力油供到起落架放下油路从软管漏出,当B系统油量<21%后,转换活门不满足作动条件回到正常位,B系统油量下降停止,由于此时A系统无法供压,导致前轮转弯无法工作。
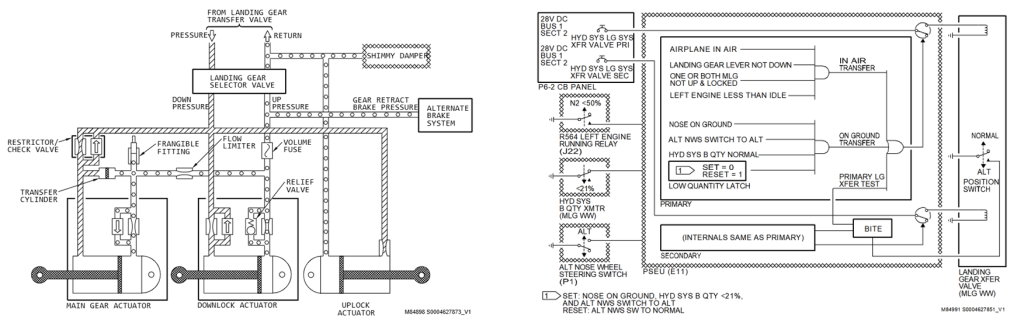
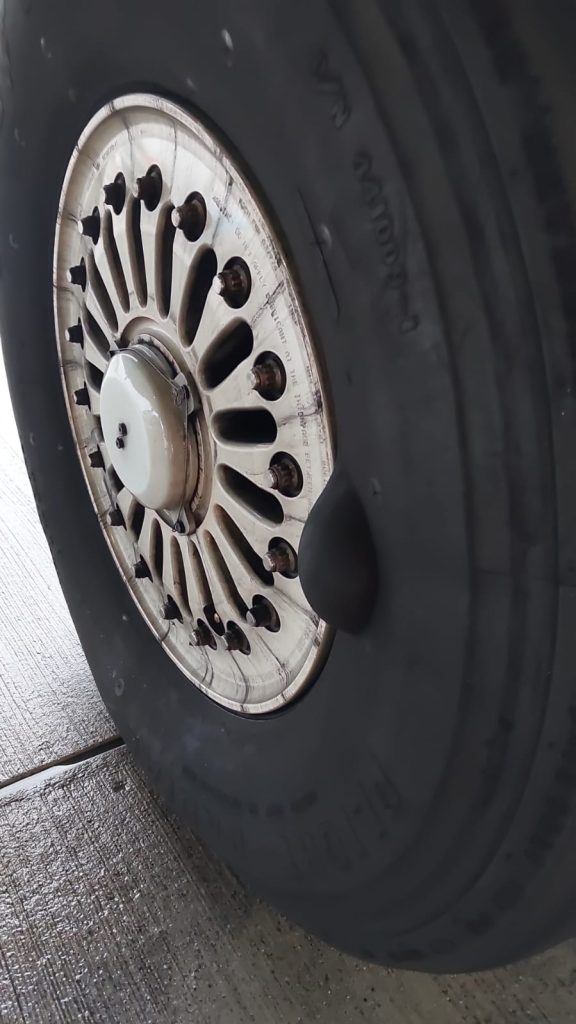
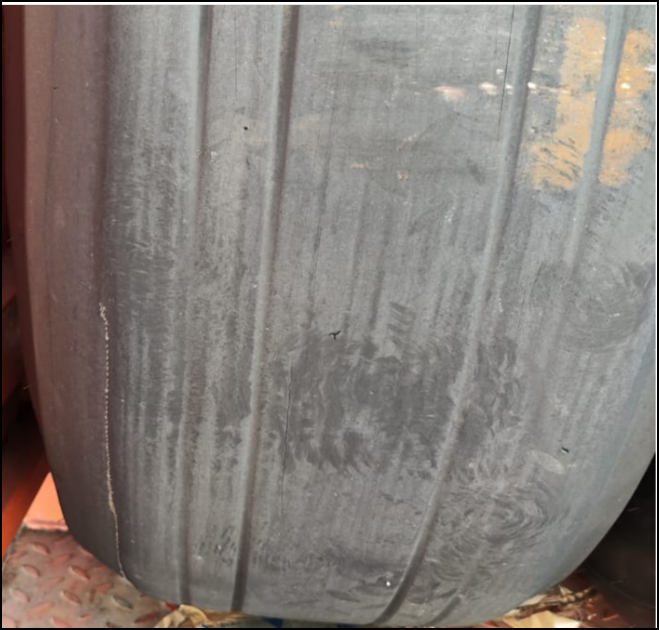
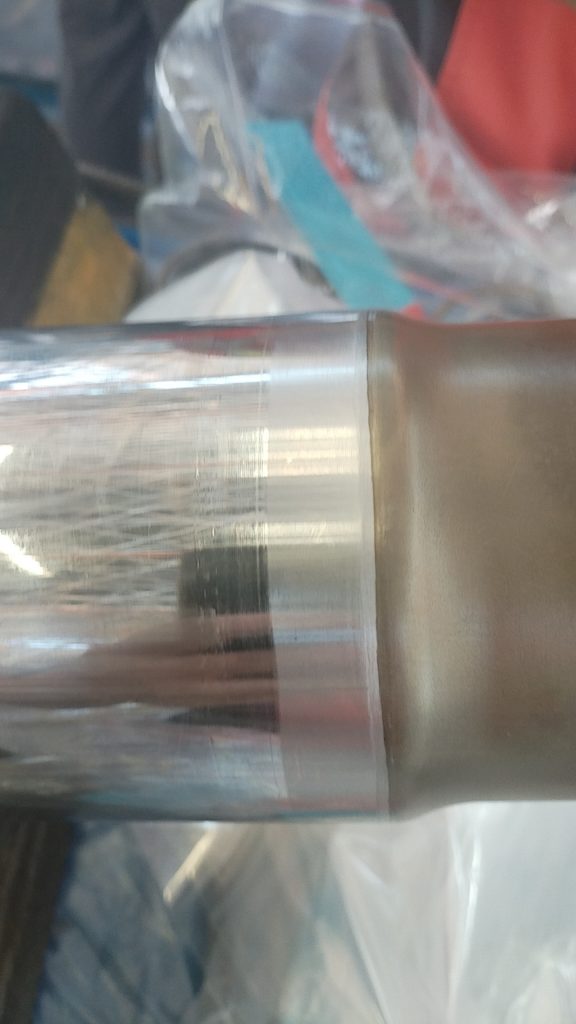
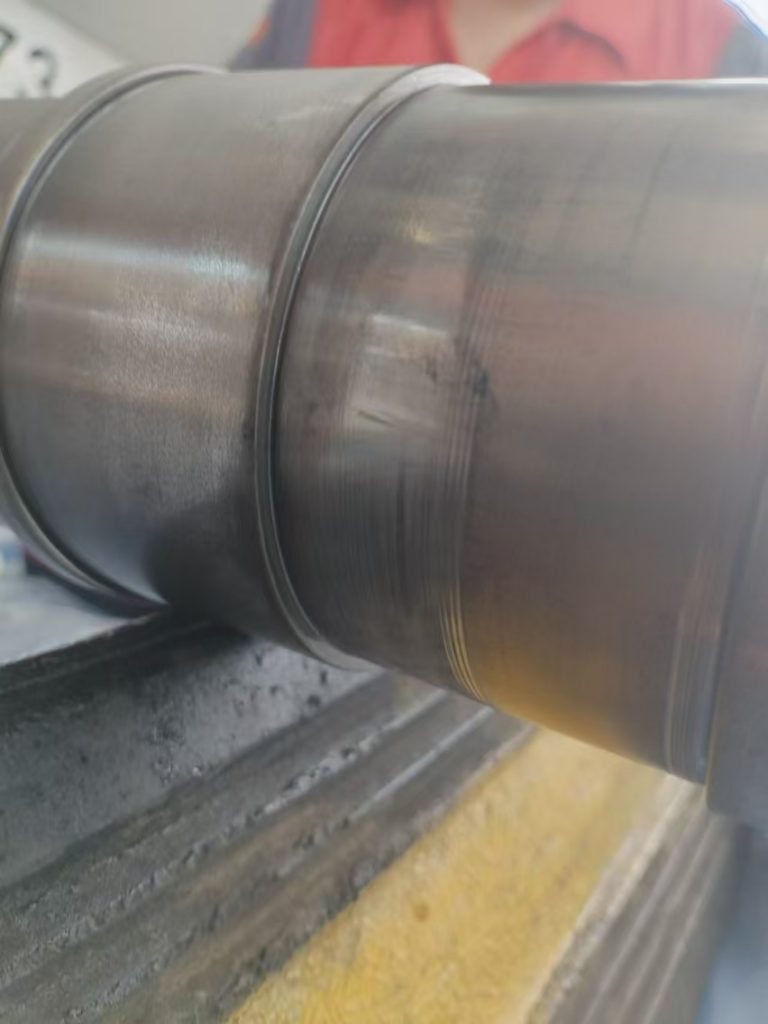
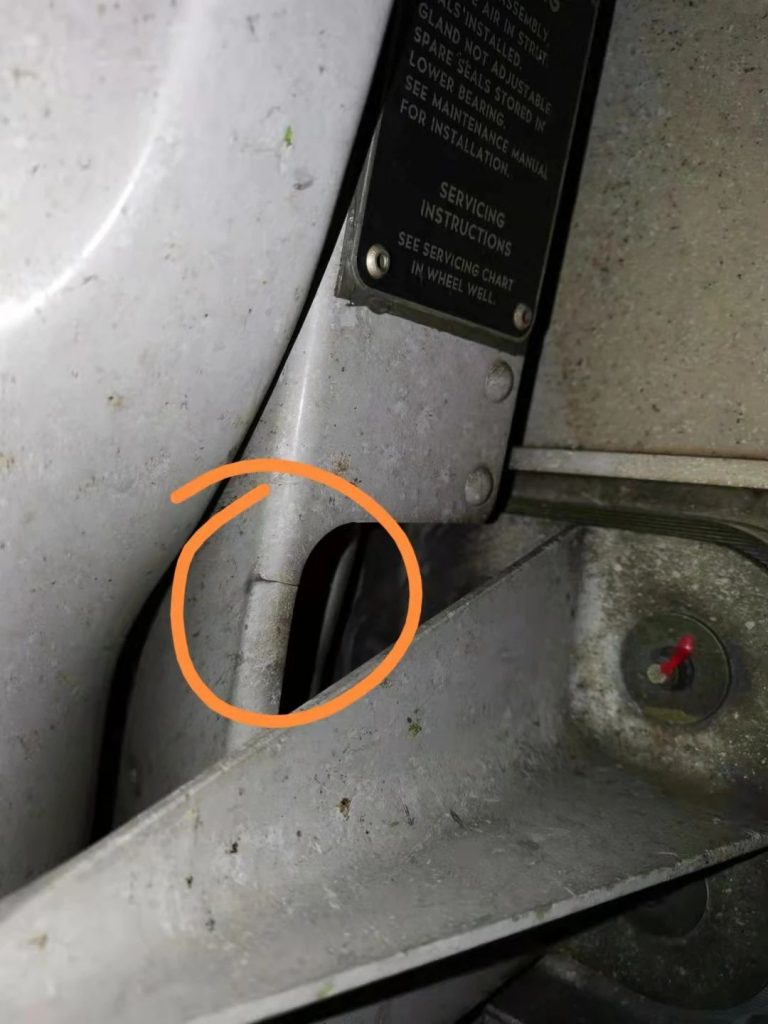
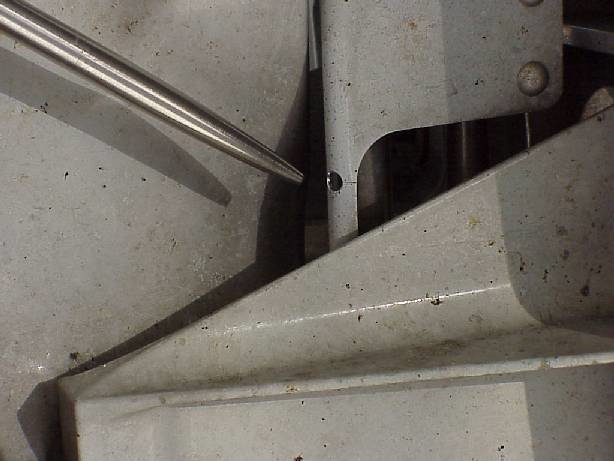
典型损伤一
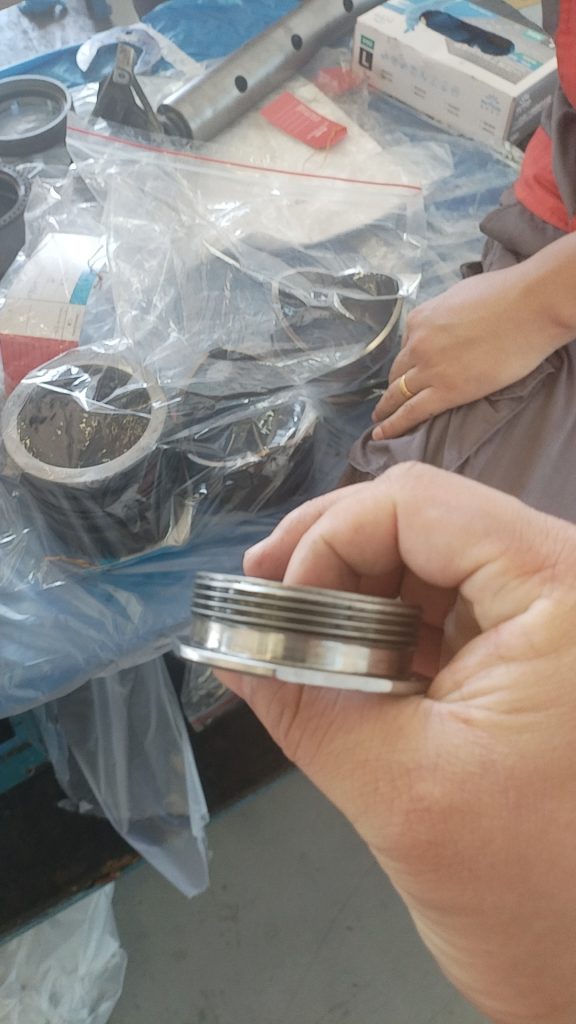
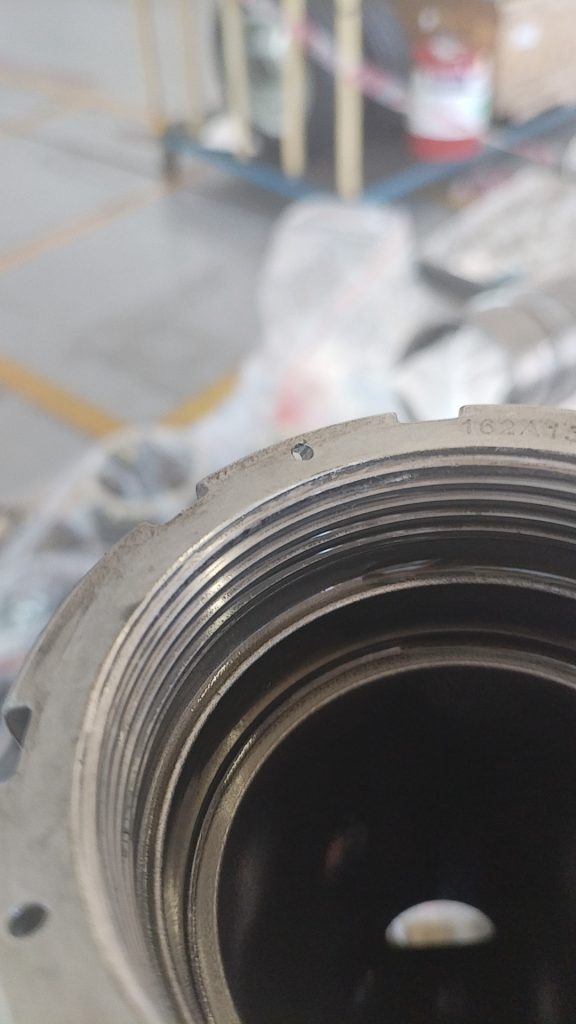
收放作动筒放下液压软管和安装在作动筒上的导向支架发生干涉,导向支架孔边缘磨损变色,液压软管外部胶皮磨穿,内部金属编织网出现断丝,扎破内部管路导致漏油。可以通过松紧卡箍调整导向支架位置,从而避免和管路发生挤压接触和磨损。

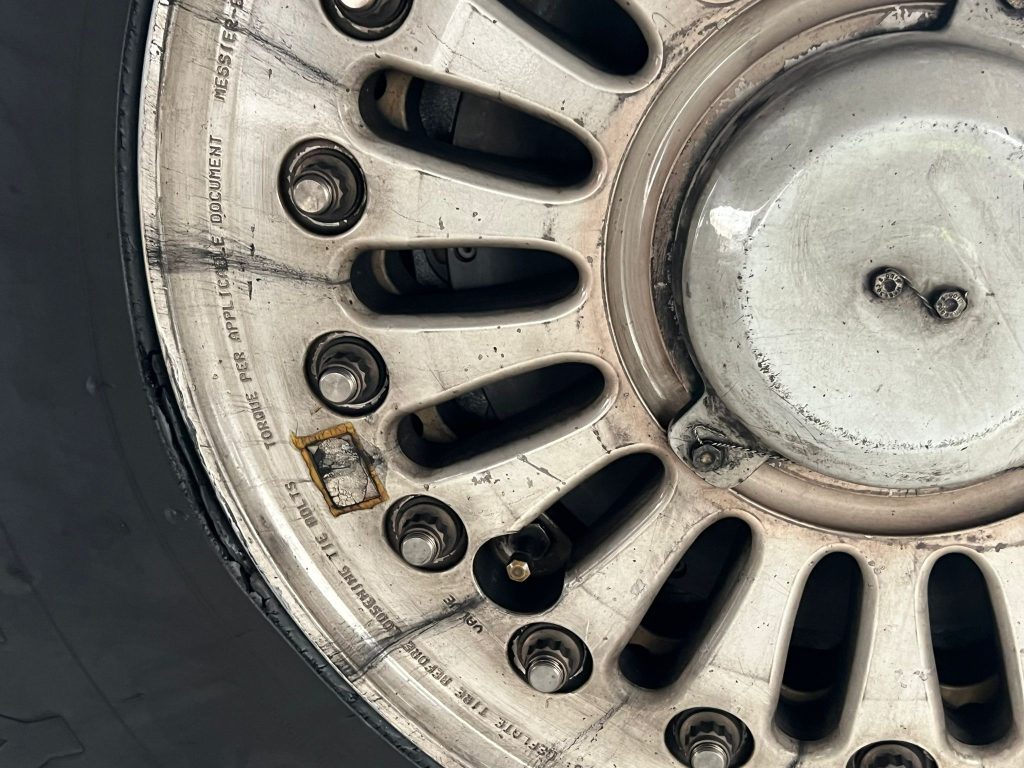
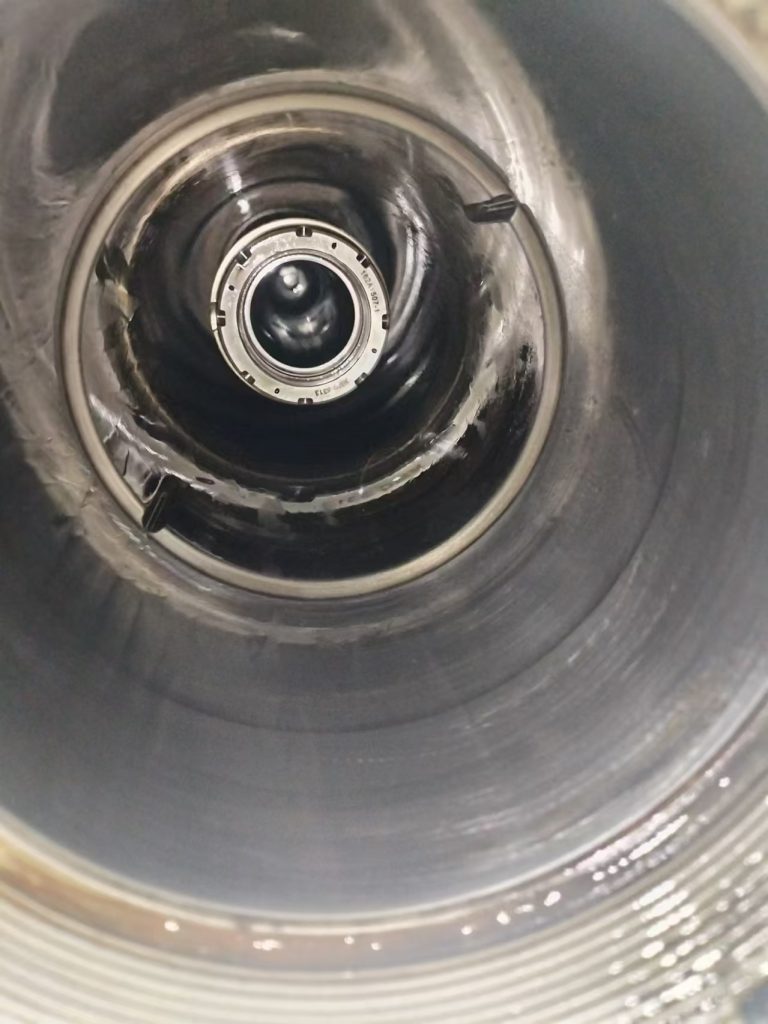
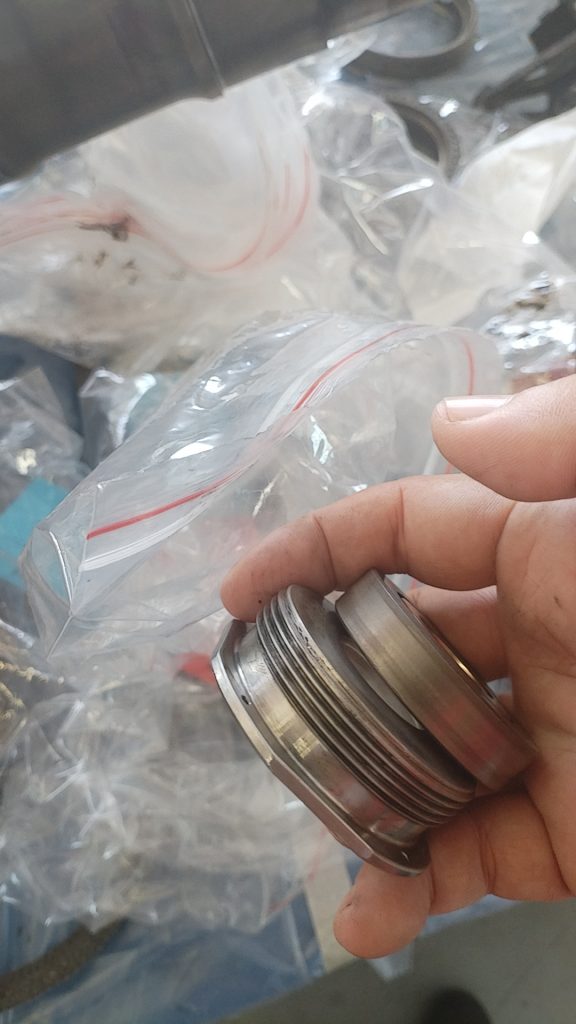
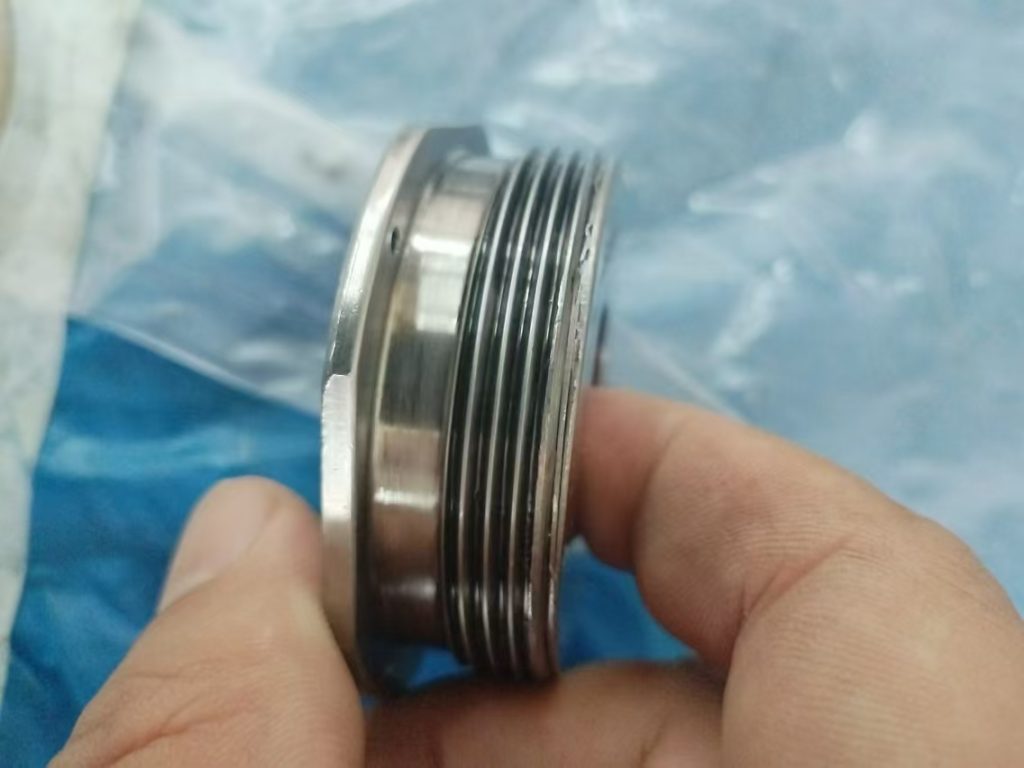
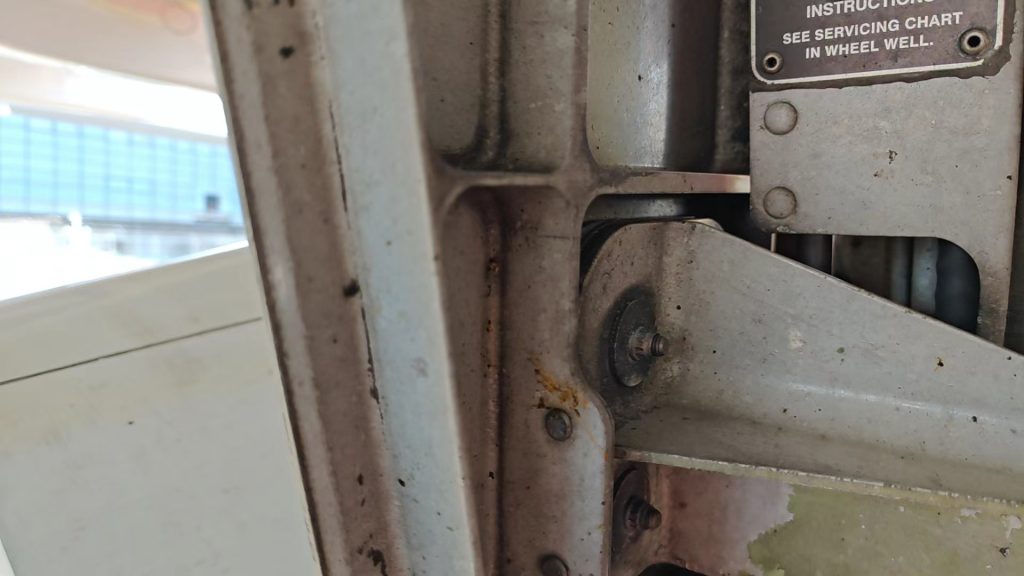
典型损伤二
通过机队普查发现起落架上方的刹车软管和导向支架也同样存在干涉,出现胶皮磨损,可见内部金属编织网的情况。可以通过调节管路固定卡子的方式调整管路和支架之间的间隙,避免干涉损伤。

手册要求
1、参考AMM 20-10-52/401 Flexible Hose – Removal/Installation 安装液压软管,以避免在拧紧软管端部紧固件时发生扭结和扭曲。
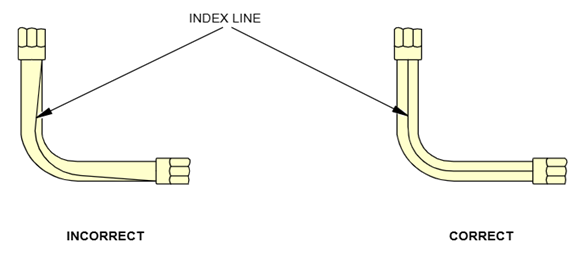
2、参考AMM 20-10-52/201 Flexible Hose – Maintenance Practices 执行液压软管的检查,确认没有扭曲、擦伤、腐蚀、断丝、漏油等,根据缺陷的损伤情况进行处置。

3、参考AMM 20-10-52/801 Hydraulic Tubing Repair 确保管路有足够的松弛度、弯曲、间隙、和足够的支撑,并且没有扭曲或弯曲。
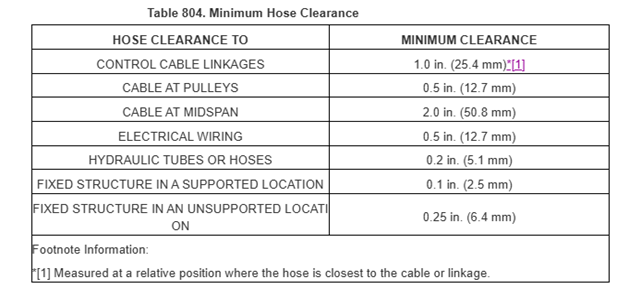
措施
为避免软管漏油对机队运行造成的影响,除例行检查措施外,已针对相关的EO和MP工卡进行改版,加入了主起收放液压软管和刹车软管的专项检查步骤,确认管路无漏油和干涉磨损的情况,具体如下:
1)73N-29-SYS-003 每4800FH详细检查主轮舱和前轮舱区域的液压部件和液压管路的安装是否牢固,有无损和渗漏。
2)EO-73N-29-2024-004/EO-73M-29-2024-003 每30天详细检查主轮舱液压部件。
一线人员在执行液压软管日常维护工作时,需注意参考AMM手册和MP工卡要求进行管路检查和更换,避免运行中管路磨损导致的漏油事件。
附:737-SL-29-122
波音曾发布737-SL-29-122对2013年1月到2014年2月之间生产的飞机,认为存在管路安装问题。本机不在1其列。
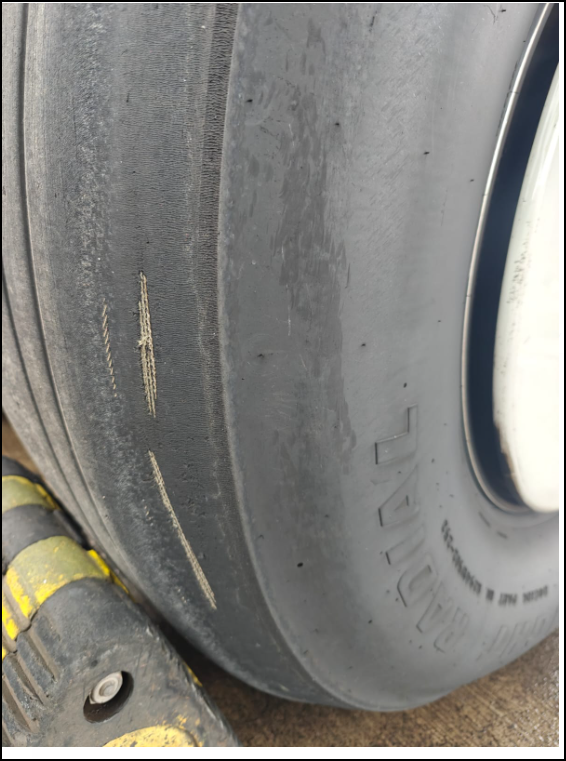
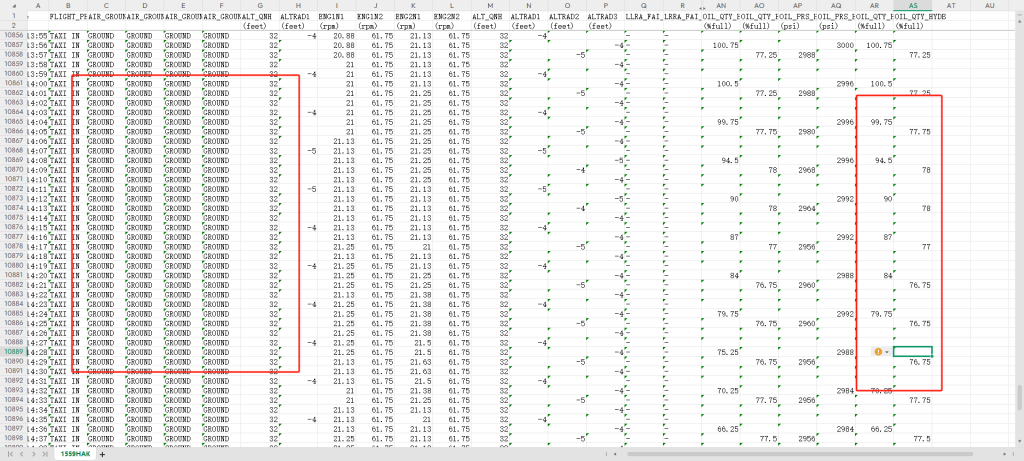
2025年5月案例补充,15*9(738)飞机,落地后A系统渗漏,B系统剩余17。软管爆裂件号:AS115-06F0324,与周边无干涉。
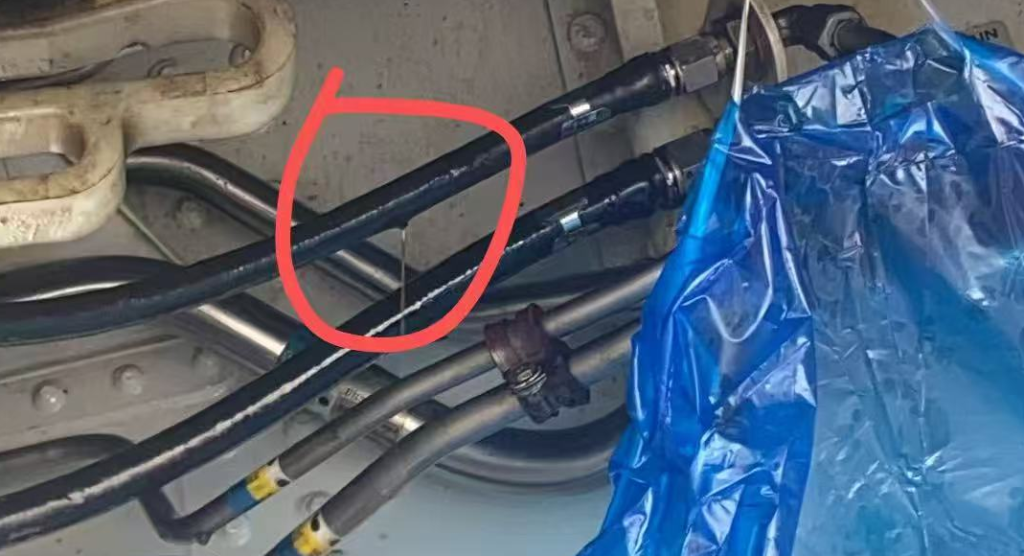

译码看发生在落地后